Epigenetics & Ecotoxicology
Exploring Epigenetics as a Tool for Ecotoxicological Work
2025-10-21
Overview
What happens when environmental exposure leaves a molecular “memory”?
How do these changes get passed on to offspring?
What role can epigenetics play in ecotoxicology work?

Image credit: OSHA
What Is Ecotoxicology?
Interdisciplinary science that interrogates nature, effects and the interaction of substances harmful to the environment
Pivoting from ocean warming, acidification and biotoxins to focus on contaminants
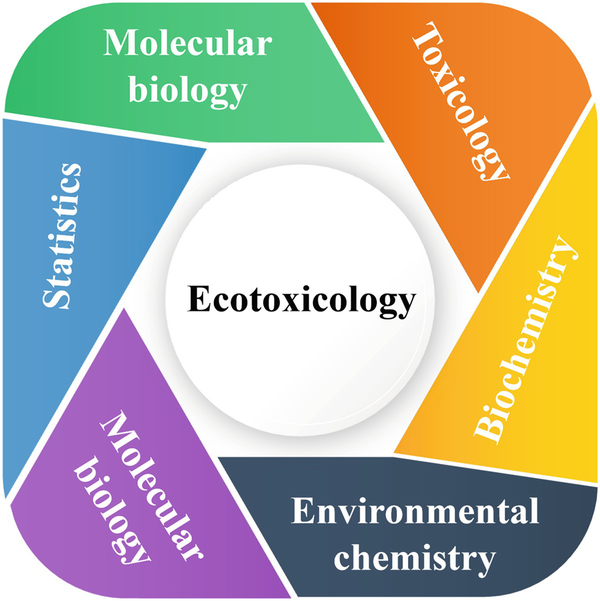
Image credit: Ecotoxicology and Risk Assessment of Contaminated Water, Springer 2024
Ecotoxicology
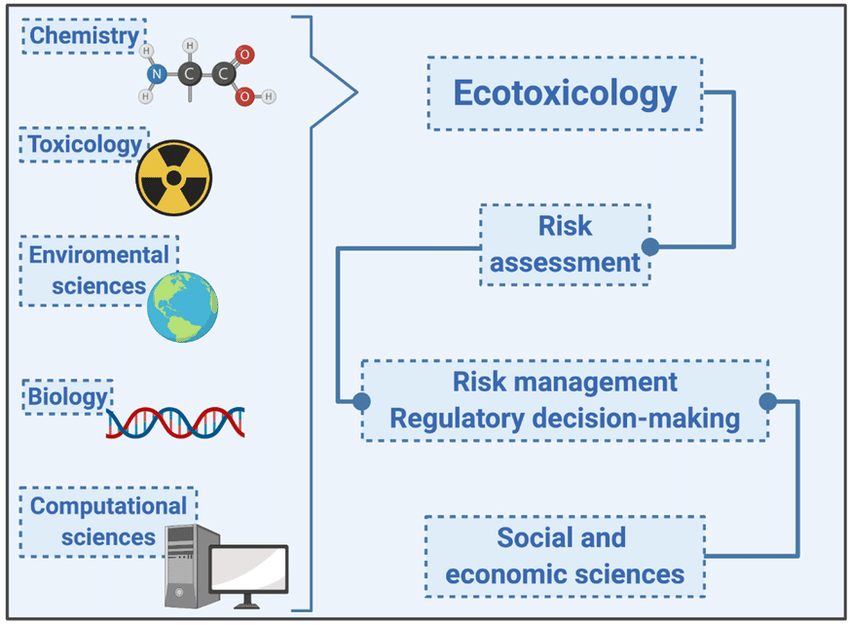
Image credit: Major interdisciplinary approaches in ecotoxicology; adapted from Amiard-Triquet et al., 2015
Environmental Epigenetics & AOPs
- Epigenetic markers can serve as biomarkers of exposure
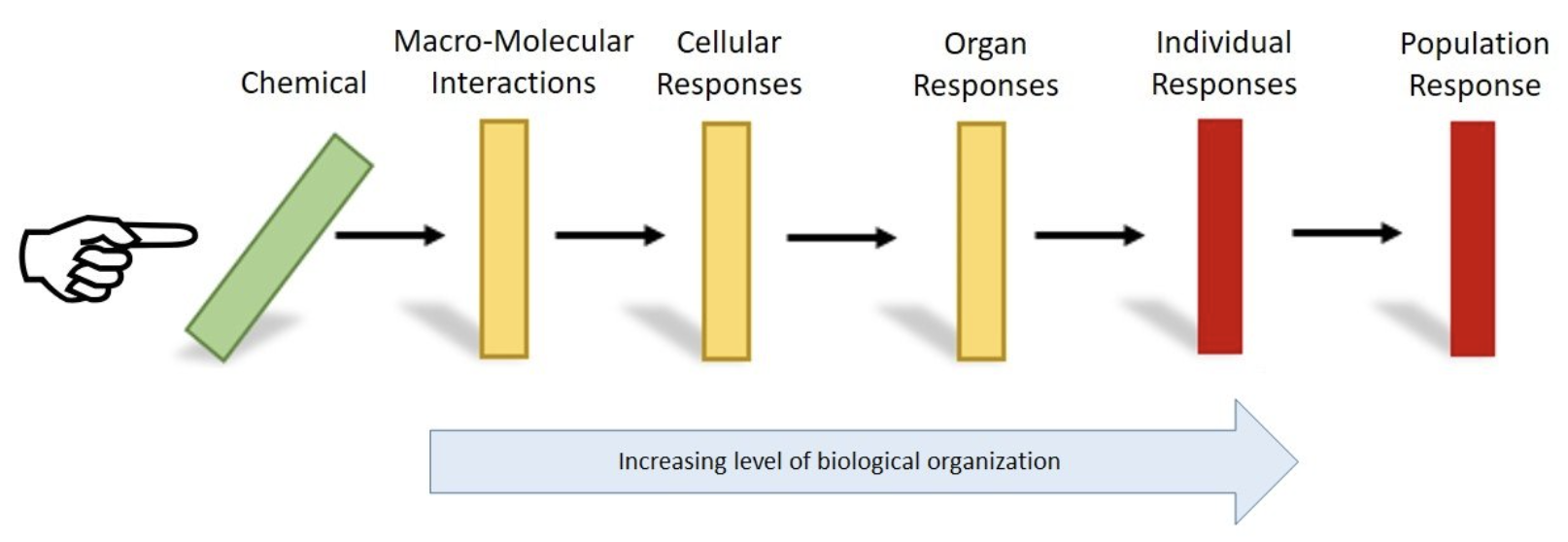
Image credit: EPA
Key Takeaway: Environmental stressors leave “molecular footprints” that link ecology and physiology
Knowledge Gap
(outlined by Chatterjee, Gim & Choi, 2018)
- Many studies show epigenetic shifts after exposure
- How long do these changes last?
- Do they influence offspring phenotype?
- Can they be inherited across generations?
Can Experience Be Inherited?
“If a parent is exposed to pesticides, could its grandchildren be affected—even if they never encounter those chemicals?”
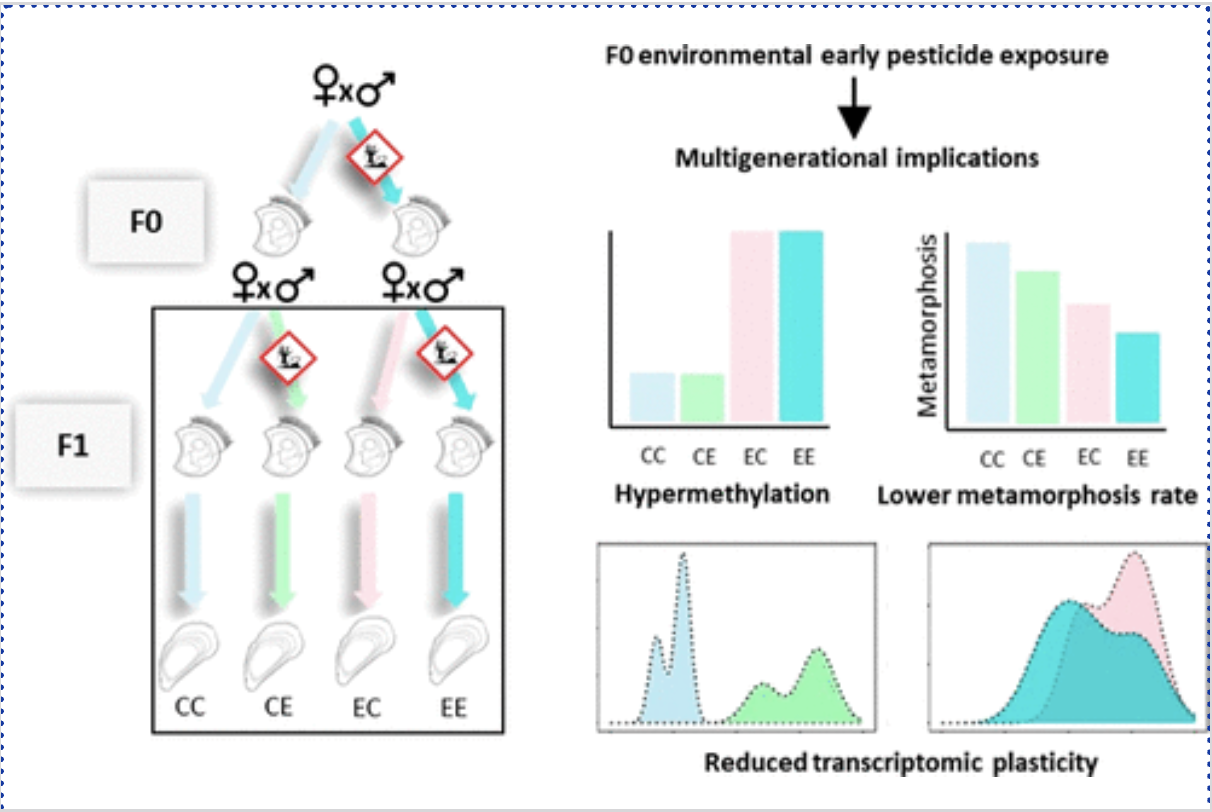
Key idea: environmental exposures can alter gene expression without changing DNA sequence
Image credit: Sol Dourdin et al., 2023
Case Study: “Ancestor’s Gift”
From Sol Dourdin et al. (2023)
- Organism: Crassostrea gigas aka the Pacific Oyster
- Exposure: early-life parental exposure to a realistic pesticide mixture
- Goal: determine whether this alters offspring phenotype and gene expression
Methods Snapshot
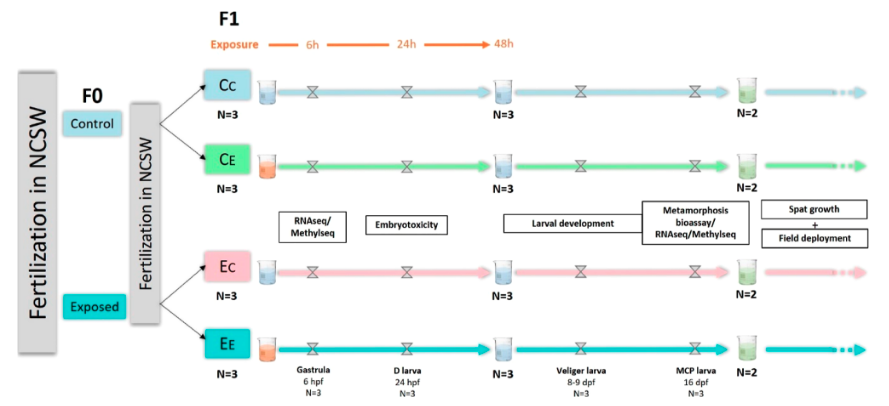
- Parental (F0) exposure → offspring (F1) analysis
- Measures included:
- Growth/morphology, behavior/stress response, & methylation/ gene expression profiling
- Controlled design mimicking environmentally relevant concentrations
Image credit: Sol Dourdin et al., 2023
Key Findings
- Offspring from exposed parents showed:
- Altered phenotype (e.g., reduced growth or altered behavior)
- Epigenetic changes linked to exposure
- No DNA sequence changes — effects are epigenetic
- Suggests intergenerational inheritance of pesticide effects

Synthesis: Connecting the Two Papers
| Concept | Review Paper | Research Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanisms | DNA methylation, histone mods, ncRNAs | DNA methylation & gene expression |
| Focus | Framework for ecotoxicology | Experimental validation |
| Outcome | Environmental memory | Transgenerational phenotype |
Epigenetic mechanisms act as the bridge between exposure and inheritance.
Broader Implications
- Redefines how we think about toxicity and risk
- Epigenetic inheritance adds a temporal dimension to environmental science
- Raises ethical and policy questions:
- Should chemical testing consider effects in future generations?